Melasma: Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment.
What is Melasma?
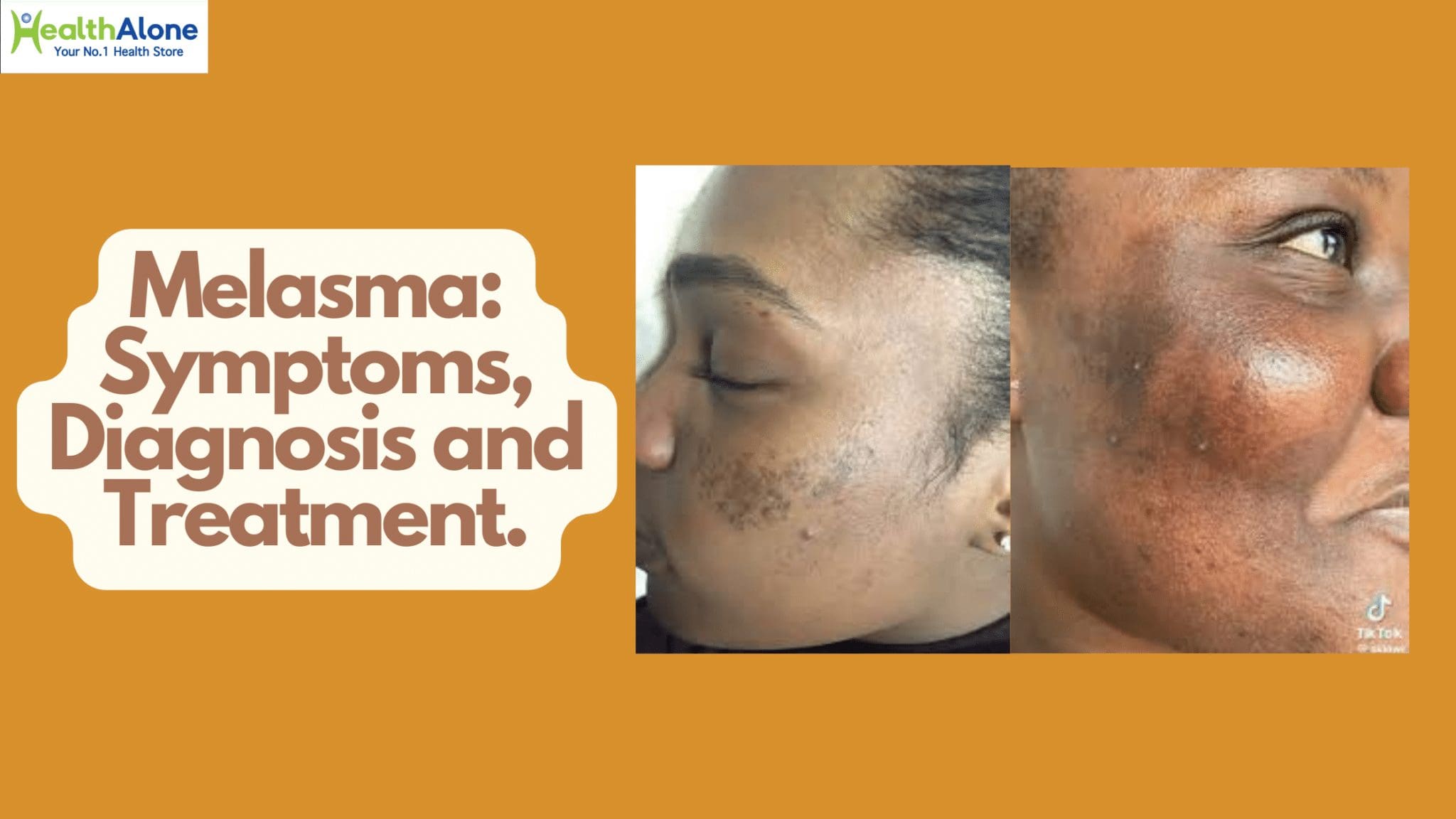
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by brown or blue-gray patches or freckle-like spots.
It’s often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy” because it frequently occurs in pregnant women, though it can affect anyone.
Melasma is typically found on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip, but it can also appear on other parts of the body that are exposed to the sun, such as the forearms and neck.
Causes of Melasma
The exact cause of melasma remains unclear, but it is believed to be the result of the overproduction of melanin, the pigment that gives color to our skin, hair, and eyes.
Several factors can trigger or exacerbate melasma, including:
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun stimulates melanocytes, which produce melanin, leading to melasma.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, use of oral contraceptives, or hormone replacement therapy can trigger melasma.
- Genetics: There is often a familial predisposition to melasma.
- Medications and Cosmetics: Certain drugs and skin care products can induce photosensitivity, making the skin more susceptible to melasma.
- Stress and Thyroid Disease: These factors can also contribute to the development of melasma.
Symptoms and Characteristics
Melasma manifests as dark, irregularly shaped patches on the skin. The patches are usually symmetrical, appearing on both sides of the face.
The most common areas affected include:
- Forehead: Often in a centrofacial pattern.
- Cheeks: Particularly along the cheekbones.
- Upper Lip: A distinctive characteristic of melasma.
- Nose and Chin: Less commonly affected but can be involved.
Who is Affected by Melasma?
Melasma predominantly affects women, especially those with darker skin types (Fitzpatrick skin types IV to VI) such as Hispanic, Asian, Middle Eastern, African, Mediterranean, and Indian women.
However, it can also affect men, accounting for about 10% of all cases. The condition is most common in adults between the ages of 20 and 50.
Types of Melasma
Epidermal Melasma
Epidermal melasma is characterized by an excess of melanin in the superficial layers of the skin (the epidermis).
It appears as well-defined, dark brown patches and is usually more responsive to treatment compared to other types.
Dermal Melasma
Dermal melasma involves deeper layers of the skin (the dermis), where melanophages (cells that ingest melanin) are present.
It appears as light brown or bluish patches and is typically more challenging to treat.
Mixed Melasma
Mixed melasma is the most common type and involves both the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin.
It presents with a combination of dark and light brown patches and may respond variably to treatment depending on the depth of pigmentation.
Other Variants
In addition to the primary types, there are other less common variants of melasma, which may be influenced by unique triggers or environmental factors.
Understanding these variations can help in customizing treatment approaches.
Diagnosing Melasma
Clinical Examination
A dermatologist can usually diagnose melasma through a physical examination of the affected areas.
The characteristic pattern and distribution of the patches often provide sufficient information for diagnosis.
Wood’s Lamp Examination
A Wood’s lamp examination involves using ultraviolet light to examine the skin. This can help determine the depth of pigmentation and differentiate between epidermal and dermal melasma, guiding appropriate treatment options.
Biopsy
In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis of melasma. This involves taking a small sample of skin for microscopic examination.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is crucial to distinguish melasma from other hyperpigmentation disorders such as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, lentigines, or pigmentary demarcation lines.
Accurate diagnosis ensures effective and targeted treatment.
Treatment Options for Melasma
Topical Treatments
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is considered the gold standard for treating melasma.
It works by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is necessary for melanin production.
Typically, a 4% hydroquinone cream is applied to the affected areas.
Retinoids
Retinoids, such as tretinoin, help increase skin cell turnover, promoting the shedding of pigmented cells.
They are often used in combination with other topical agents for enhanced effectiveness.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and lighten hyperpigmented areas. They are sometimes included in combination creams with hydroquinone and retinoids.
Oral Treatments
Tranexamic Acid
Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic agent that has shown promise in treating melasma. It can be administered orally or applied topically, helping to reduce pigmentation.
Oral Contraceptives
For women whose melasma is triggered by hormonal fluctuations, switching to a different form of birth control or discontinuing oral contraceptives may help reduce pigmentation.
Procedural Treatments
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin to remove the outer layer and promote the growth of new, less pigmented skin. Common agents used include glycolic acid, salicylic acid, and trichloroacetic acid.
Laser Therapy
Laser treatments, such as Q-switched Nd lasers, target melanin in the skin to break up pigment particles.
This treatment should be performed by experienced dermatologists to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure that exfoliates the skin, helping to reduce pigmentation and improve skin texture. It is often used in combination with other treatments for better results.
Natural and Home Remedies
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera contains aloin, a natural depigmenting compound that can help lighten melasma. Regular application of aloe vera gel can soothe and improve the appearance of the skin.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar contains acetic acid, which may help lighten pigmentation. Diluting it with water and applying it to the skin can offer mild exfoliation and lightening effects.
Turmeric
Turmeric has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can benefit the skin. A turmeric paste or mask can be used to help reduce pigmentation and improve skin tone.
Green Tea Extracts
Green tea extracts contain polyphenols, which have been shown to inhibit melanin production. Topical application of green tea extracts can help reduce the appearance of melasma.
Sun Protection
Sun protection is crucial in managing and preventing melasma. Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun hours can significantly reduce the risk of melasma.
Preventing Melasma
Sun Protection Measures
Consistent and rigorous sun protection is the most effective way to prevent melasma. This includes using sunscreen daily, seeking shade, and wearing hats and sunglasses.
Skincare Routine
A gentle skincare routine that includes non-irritating products can help maintain skin health and prevent melasma. Avoiding harsh exfoliants and using products designed for sensitive skin can be beneficial.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can support skin health. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and fish can help protect the skin from further damage and support its natural healing processes.
Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding known triggers, such as certain medications or cosmetic products, can help prevent the onset or worsening of melasma. Consulting with a dermatologist to identify potential triggers is advisable.
Melasma and Pregnancy
Chloasma: The Mask of Pregnancy
Melasma that occurs during pregnancy is often referred to as chloasma or the “mask of pregnancy.”
Hormonal changes, particularly increased levels of estrogen and progesterone, are significant contributors to this condition.
Chloasma typically appears during the second or third trimester and may fade after childbirth.
Managing Melasma During Pregnancy
Managing melasma during pregnancy requires a careful approach to avoid harming the mother or the baby. Safe options include:
- Sun Protection: Using physical sunscreens containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
- Gentle Skincare: Utilizing mild, non-irritating products.
- Topical Agents: Products like azelaic acid, which is considered safe during pregnancy.
Post-Pregnancy Treatment
After pregnancy, many women seek more aggressive treatments to reduce melasma. These may include:
- Resuming Topical Treatments: Hydroquinone and retinoids.
- Procedural Treatments: Laser therapy or chemical peels.
- Oral Treatments: Tranexamic acid, under medical supervision.
Psychological Impact of Melasma
Emotional Well-being
Melasma can significantly impact an individual’s self-esteem and emotional well-being. The visible nature of the condition, especially on the face, can lead to feelings of self-consciousness, anxiety, and even depression.
Coping Strategies
Developing effective coping strategies is essential for managing the psychological impact of melasma. These strategies may include:
- Seeking Support: Talking to friends, family, or support groups.
- Therapeutic Interventions: Engaging in counseling or therapy.
- Positive Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and stress management techniques.
Support Groups and Resources
Support groups and online communities can provide a platform for sharing experiences and receiving encouragement from others facing similar challenges. Resources like the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases offer valuable information and support.
Melasma in Men
Prevalence and Characteristics
While melasma is more common in women, it does affect men. Men with darker skin types and those living in sunny climates are more prone to developing melasma. The presentation and triggers of melasma in men are similar to those in women, though hormonal factors are less prominent.
Treatment Considerations
Treatment for melasma in men generally follows the same protocols as for women, but with additional considerations for skincare routines and any underlying health issues. Men may also benefit from lifestyle adjustments to manage sun exposure and skin health.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
New Treatment Modalities
Ongoing research continues to explore new treatment modalities for melasma. Innovations in topical formulations, such as new depigmenting agents and combination therapies, are showing promise in improving outcomes for patients.
Genetic Studies
Genetic studies are shedding light on the hereditary aspects of melasma. Understanding the genetic factors involved can lead to more personalized treatment approaches and preventative measures.
Technological Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment
Advances in technology, including improved laser devices and non-invasive imaging techniques, are enhancing the ability to diagnose and treat melasma more effectively. These innovations offer hope for better management of this challenging condition.
Personal Stories and Experiences
Testimonials
Hearing from individuals who have successfully managed their melasma can be inspiring and informative. Personal testimonials provide real-world insights into the effectiveness of various treatments and coping strategies.
Case Studies
Detailed case studies of patients with melasma, including their treatment journeys and outcomes, can offer valuable lessons for others. These studies highlight the importance of personalized treatment plans and the potential for successful management of melasma.
Myths and Facts about Melasma
Common Misconceptions
There are many myths surrounding melasma, such as the belief that it only affects pregnant women or that it is caused by poor hygiene. Dispelling these myths is important for better understanding and managing the condition.
Evidence-based Facts
Providing evidence-based facts about melasma helps educate the public and promote informed decision-making. This includes understanding the role of sun exposure, hormonal influences, and effective treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Common Queries and Concerns
Addressing common queries and concerns about melasma can help alleviate anxiety and confusion. Frequently asked questions may include:
- Is melasma curable?
No, melasma isn’t curable, but its appearance can be managed and reduced with treatment.
- Can melasma come back after treatment?
Yes, melasma can return after treatment, especially if triggers like sun exposure are not avoided.
- What is the best sunscreen for melasma?
The best sunscreen for melasma is a broad-spectrum (UVA and UVB) sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, preferably with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
- Are there any natural treatments that work?
Yes, natural treatments like aloe vera, vitamin C, licorice extract, niacinamide, and turmeric may help lighten melasma but are generally less effective than prescription treatments.
Conclusion
Melasma is a complex and multifaceted skin condition requiring a comprehensive management and treatment approach.
Understanding its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for those affected by this condition.
With ongoing research and advances in treatment, there is hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals with melasma.




